TABLE OF CONTENTS
1. XPath Overview
XPath is defined as XML path. It is a syntax for finding UI elements on a web page using the XML path expression, commonly known as a locator.
1.1 Syntax for XPath
XPath contains the path of the element situated on the web page.
The standard syntax for creating XPath is as follows:
XPath=//tagname[@attribute='value']
This expression is used to identify an element based on its tag name and a specific attribute-value pair. For more information, refer to the article on the Perfecto blog.
Note: In the automation workflow, it's essential to balance the use of both relative and absolute XPaths. However, it is recommended to use relative paths for ease of maintenance.
2. Locator Mapping
Locator Mapping is a functionality that allows users to manage and update locators, specifically XPath expressions, associated with UI elements in an application. When there is a change in the application or if a locator is no longer effective, Locator Mapping provides a way to replace or update these locators.
For example, if the existing locator mapped in the Object repository file for an Email ID isn't working after a recent change to an application, then you can perform the following steps:
- On the Left Pane, navigate to the Object Repository.
- Click on Locator Mapping which is available in top right corner.
- The Locator Mapping screen appears. In this screen, click the 'cloud' icon to upload the scraped file in the CSV format or you can drag the scraped file.
 Search functionality: If you have uploaded a large CSV file and wish to search for a required UI element, you can use search functionality.
Search functionality: If you have uploaded a large CSV file and wish to search for a required UI element, you can use search functionality.
 Ensure to upload a CSV file with all the scraped UI element details.
Ensure to upload a CSV file with all the scraped UI element details.
- Here you'll see existing scraped file details from the Object Repository file and uploaded re-scraped file details. In this screen, choose the appropriate UI element name in the CSV file. Select the matching UI element or elements with Control Type displayed in the Object Repository file pane.
Click Remove button on the top if you wish to replace and add a new scraped file. You can also search for a particular UI element in the search bar.
If you use invalid values in the search bar in the Re-scraped file details pane and Object Repository file details pane, you will see following error messages:
Ensure that your search criteria are accurate and relevant to the data you're trying to retrieve. - Click
 icon to view the updated locator information and if you wish to remove updated locator information, then click minus icon.
icon to view the updated locator information and if you wish to remove updated locator information, then click minus icon.
- Click the save icon to view the changes in the Object Repository file and corresponding locator information in the Node configuration.
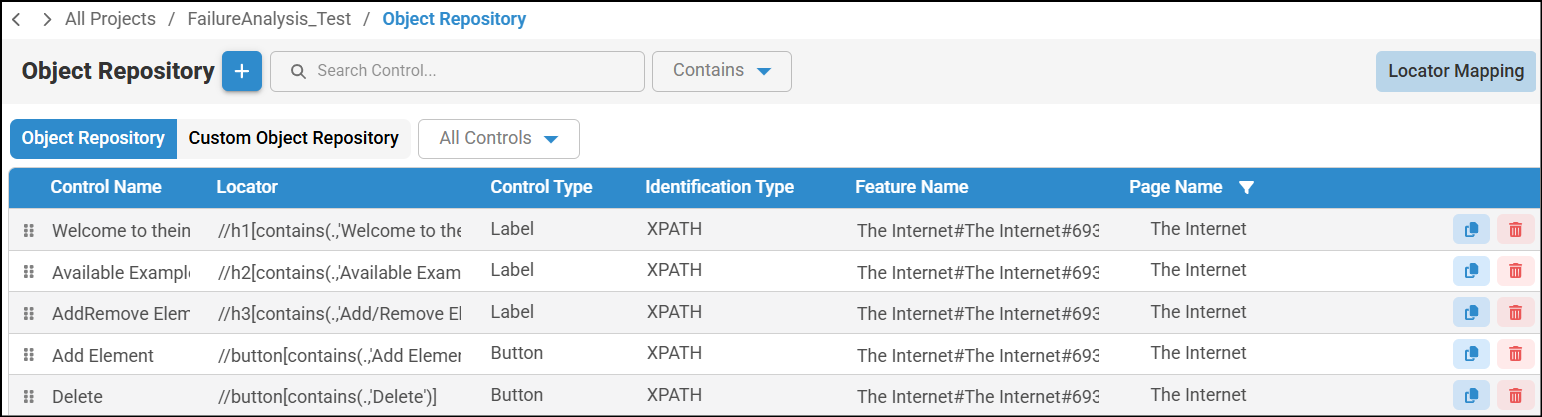
- To access Object Repository file, navigate to Object Repository in left pane to view the updated locator information.
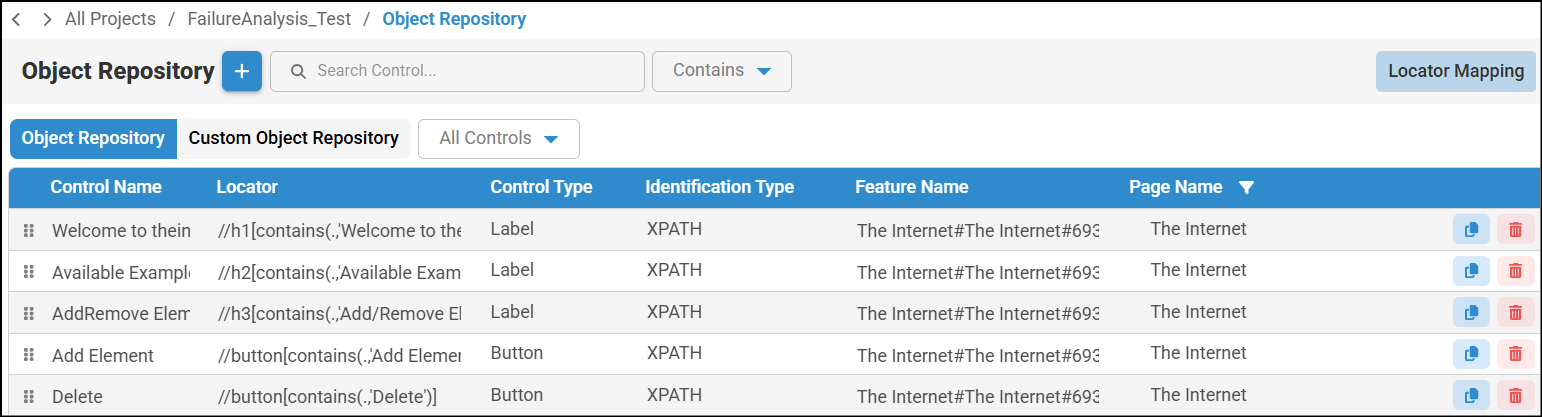
- To access Controls, navigate to the appropriate Node>click on the node to view Control. In this window, appropriate locator information will be updated.
- In the Test Design feature, you have the option to assign an alias name to a UI element and update its associated Locator information using this feature. Note that any changes you make will only affect the UI element associated with the alias name in the Object Repository. The original XPath expression for the UI element remains unchanged in Node Configuration and Object Repository.
The Locator mapping feature is specific to the UI elements name, type, and XPath expression. For example, when multiple controls share the same UI element name but different XPaths or UI element types, and if you map an XPath to one of these UI elements in the Locator Mapping feature, the XPath will be updated for that particular UI element with its specific UI element type and XPath. The XPaths of other UI elements with the same name but different XPath expressions or UI element types remain unchanged.
Was this article helpful?
That’s Great!
Thank you for your feedback
Sorry! We couldn't be helpful
Thank you for your feedback
Feedback sent
We appreciate your effort and will try to fix the article